Introduction
Sociology is one of the most popular optional subjects in the UPSC Civil Services Examination. It covers society, culture, social change, and institutions, offering candidates an opportunity to connect theory with real-life situations. Practicing questions from every part of the syllabus helps in mastering the subject and writing effective answers. Below are 100 important questions divided into chapters based on the UPSC Sociology syllabus.
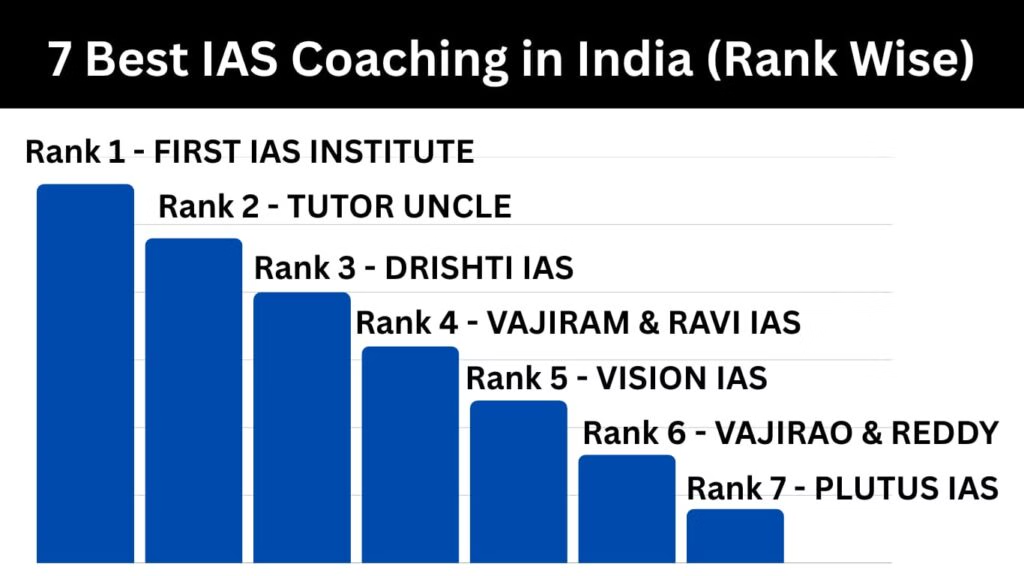
For UPSC Coaching , Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE (India’s Top IAS Coaching)
Chapter 1: Sociology – The Discipline
- Define Sociology and explain its emergence as a discipline.
- Discuss the scope of Sociology in understanding society.
- Explain the relationship of Sociology with History.
- Explain the relationship of Sociology with Political Science.
- Explain the relationship of Sociology with Economics.
- Explain the relationship of Sociology with Anthropology.
- What is the scientific method in Sociology?
- Discuss the subjectivity vs objectivity debate in Sociology.
- Explain common sense knowledge vs Sociological knowledge.
- Write short notes on Sociology as a value-neutral science.
Chapter 2: Sociology as Science
- Is Sociology a science? Discuss.
- Explain the positivist method in Sociology.
- Explain the interpretative method in Sociology.
- What are the limitations of the scientific method in Sociology?
- Discuss the use of empirical research in Sociology.
- Explain the role of statistical methods in Sociology.
- Compare Sociology with Natural Sciences.
- Compare Sociology with Social Sciences.
- Discuss the problems of objectivity in Social Research.
- Explain the meaning and role of hypothesis in Sociology.
3: Research Methods and Analysis
- Explain qualitative research methods in Sociology.
- Explain quantitative research methods in Sociology.
- What is participant observation? Discuss its merits and demerits.
- Explain content analysis as a method of sociological research.
- Discuss survey method and its limitations.
- What is a case study method? Explain with examples.
- Discuss comparative method in Sociology.
- Define sampling and explain its types.
- What are the main challenges in data collection?
- Explain reliability and validity in social research.
Chapter 4: Sociological Thinkers
- Discuss Karl Marx’s theory of historical materialism.
- Explain Marx’s concept of class struggle.
- Discuss Max Weber’s theory of social action.
- Explain Weber’s theory of bureaucracy.
- Explain Weber’s concept of authority.
- Discuss Durkheim’s concept of social facts.
- Explain Durkheim’s theory of division of labour.
- Discuss Durkheim’s views on suicide.
- Explain Mead’s theory of self.
- Discuss Parsons’ theory of social system.
- Explain Merton’s theory of deviance.
- Explain Sorokin’s views on social change.
- Discuss G.H. Mead’s theory of symbolic interactionism.
- Explain the contribution of C.W. Mills to sociological imagination.
- Discuss Habermas’s theory of communicative action.
Chapter 5: Stratification and Mobility
- Define social stratification and its types.
- Explain caste as a system of stratification.
- Compare caste and class.
- Explain Weber’s view on class, status, and power.
- Discuss Marx’s view on class struggle in modern society.
- Explain social mobility and its types.
- Discuss open and closed systems of stratification.
- Explain the role of education in social mobility.
- Discuss the impact of industrialization on stratification.
- Explain Davis and Moore’s theory of stratification.
6: Works and Economic Life
- Discuss the role of work in human society.
- Explain the changing nature of work in industrial society.
- Explain the concept of alienation as given by Marx.
- Discuss the role of technology in economic life.
- Explain the informal sector in India.
Chapter 7: Politics and Society
- Discuss the relationship between polity and society.
- Explain Weber’s theory of authority.
- Explain the concept of democracy in modern society.
- Discuss political parties as social institutions.
- Explain pressure groups and their role in democracy.
Chapter 8: Religion and Society
- Discuss the role of religion in society.
- Explain Durkheim’s theory of religion.
- Explain Weber’s views on the Protestant ethic and capitalism.
- Discuss secularization and its impact on society.
- Explain the concept of religious pluralism in India.

9: Family, Marriage, and Kinship
- Define family and its functions.
- Explain the changing nature of family in modern society.
- Discuss the forms of marriage.
- Explain the concept of kinship system.
- Discuss the impact of industrialization on family.
Chapter 10: Social Change in Modern Society
- Define social change and explain its characteristics.
- Discuss theories of social change.
- Explain the role of technology in social change.
- Explain the impact of globalization on society.
- Discuss the role of social movements in social change.
Chapter 11: Indian Society – Structure and Change
- Discuss the features of Indian society.
- Explain the unity in diversity of Indian society.
- Discuss the caste system in India.
- Explain caste-class dynamics in modern India.
- Discuss the process of Sanskritization.
- Discuss the process of Westernization.
- Explain the concept of modernization in India.
- Explain the impact of globalization on Indian society.
- Discuss the role of Panchayati Raj institutions in social change.
- Discuss the status of women in Indian society.
12: Social Issues in India
- Discuss communalism as a problem in Indian society.
- Discuss regionalism as a problem in Indian society.
- Explain the problem of caste violence.
- Explain the problem of child labour.
- Discuss the problem of poverty in India.
- Discuss the issue of dowry in India.
- Explain the problem of unemployment.
- Discuss the problem of domestic violence.
- Explain the problem of corruption in Indian society.
- Discuss the role of education in addressing social issues in India.
Conclusion
Sociology as an optional subject in UPSC covers both theoretical and applied aspects of society. These 100 questions touch on every part of the syllabus, from sociological theory to contemporary issues in Indian society. Practicing them will help aspirants develop analytical ability, structure their answers effectively, and connect classical concepts with present-day realities, thereby strengthening their preparation for the Civil Services Examination.
Also Visit – Best IAS Coaching in India
For Answer Writing Techniques – Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE

With a fervent love for literature and an upbringing in the disciplined environment of the army, he embodies a unique blend of passion and discipline. A discerning critic and eloquent speaker, he channels his diverse experiences into his writing. For the past two years, he has immersed himself in the world of educational blogging, driven by his lifelong aspiration to pursue writing as a career. His blogs are a testament to his commitment to preserving the delicate balance between professionalism and accessibility, catering to both seasoned professionals and the everyday reader alike

