Introduction
Philosophy as an optional subject in UPSC Civil Services offers a balance of conceptual depth and analytical clarity. The syllabus is divided into Indian and Western Philosophy, followed by Socio-Political Philosophy and Philosophy of Religion. Below are 100 practice questions, organized chapter-wise, to help aspirants strengthen their preparation.
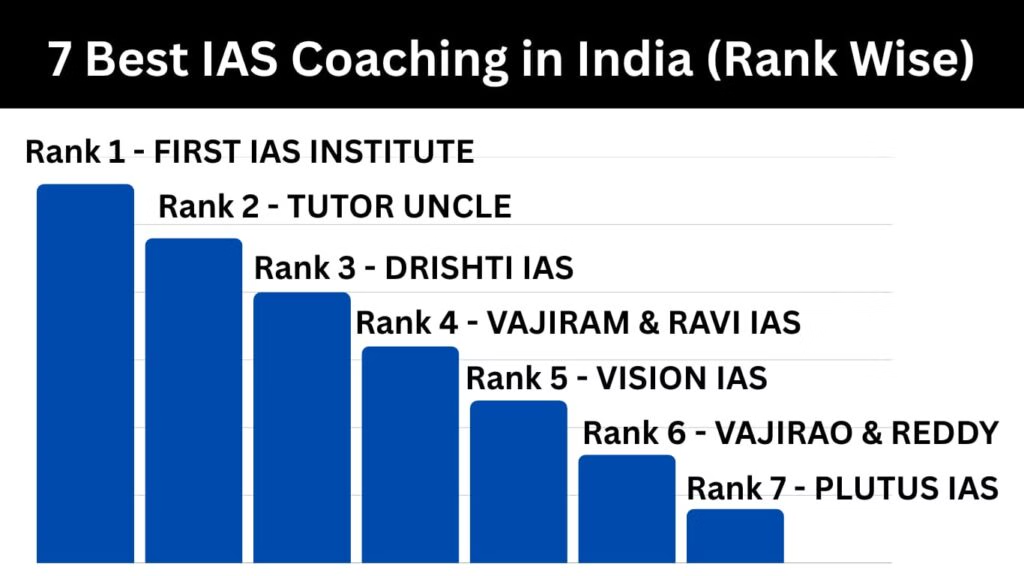
For UPSC Coaching , Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE (India’s Top IAS Coaching)
Chapter 1: Indian Philosophy
- Explain the concept of Rta in Vedic philosophy.
- What is the role of Shruti and Smriti in Indian epistemology?
- Discuss the theory of Satkaryavada in Samkhya philosophy.
- Examine the role of Purusha and Prakriti in Samkhya dualism.
- Explain the concept of Pratyaksha as a means of knowledge in Nyaya philosophy.
- What is the Nyaya theory of inference?
- Discuss the concept of Syllogism in Nyaya system.
- Explain the concept of Anumana with examples.
- Describe the Vaisheshika theory of categories (Padarthas).
- What is the atomic theory of Vaisheshika?
- Discuss the Advaita Vedanta concept of Maya.
- Explain the relation between Brahman and Atman in Shankaracharya’s philosophy.
- What is Ramanuja’s concept of Vishishtadvaita?
- Discuss Madhvacharya’s Dvaita Vedanta.
- Explain the concept of Bhakti in Indian philosophy.
- What is Mimamsa’s theory of Apurva?
- Discuss Prabhakara’s theory of knowledge.
- What is Kumarila Bhatta’s theory of error (Khyativada)?
- Explain the Buddhist theory of Pratityasamutpada.
- Discuss the Buddhist doctrine of Anatta (no-soul).
- Explain the concept of Shunyata in Madhyamaka Buddhism.
- Describe the Yogachara theory of Vijnanavada.
- What is the role of the Eightfold Path in Buddhist philosophy?
- Explain the Jain concept of Anekantavada.
- Discuss the theory of Syadvada in Jain philosophy.
Chapter 2: Western Philosophy
- Explain Plato’s theory of Ideas.
- What is Aristotle’s theory of Causation?
- Discuss Aristotle’s concept of substance.
- Explain Descartes’ method of doubt.
- What is Descartes’ Cogito ergo sum?
- Discuss Spinoza’s concept of Substance Monism.
- Explain Leibniz’s Monadology.
- What is Locke’s theory of knowledge?
- Explain Locke’s theory of primary and secondary qualities.
- Discuss Berkeley’s subjective idealism.
- Explain Hume’s theory of causation.
- What is Kant’s distinction between phenomena and noumena?
- Discuss Kant’s theory of categories.
- Explain Kant’s moral philosophy (Categorical Imperative).
- Discuss Hegel’s dialectical method.
- Explain Hegel’s concept of Absolute Spirit.
- Discuss Schopenhauer’s concept of Will.
- Explain Nietzsche’s idea of the Will to Power.
- Discuss Nietzsche’s critique of morality.
- Explain Karl Marx’s concept of historical materialism.
- Discuss Marx’s theory of alienation.
- Explain John Stuart Mill’s Utilitarianism.
- What is Jeremy Bentham’s Hedonistic calculus?
- Discuss Sartre’s concept of freedom and responsibility.
- Explain Simone de Beauvoir’s feminist existentialism.
3: Socio-Political Philosophy
- Explain the concept of justice in social philosophy.
- Discuss Plato’s theory of justice in the Republic.
- Explain Aristotle’s concept of state and citizenship.
- Discuss Rousseau’s idea of the General Will.
- What is Hobbes’ theory of Social Contract?
- Explain Locke’s social contract theory.
- Discuss the Marxist view of state.
- What is Rawls’ theory of justice?
- Explain Nozick’s entitlement theory.
- Discuss the concept of rights in modern political philosophy.
- What is the difference between negative and positive liberty?
- Explain Isaiah Berlin’s concept of liberty.
- Discuss the Gandhian concept of Sarvodaya.
- What is Gandhi’s theory of Satyagraha?
- Discuss Ambedkar’s views on social justice.
- Explain the role of equality in political philosophy.
- What is the difference between formal and substantive equality?
- Discuss affirmative action in social justice.
- Explain the idea of secularism in Indian political thought.
- What is the concept of democracy as per Western philosophy?
- Discuss participatory democracy vs representative democracy.
- Explain liberalism and its critiques.
- Discuss communitarianism in political philosophy.
- What is the feminist critique of political philosophy?
- Explain the role of multiculturalism in socio-political thought.

Chapter 4: Philosophy of Religion
- Discuss the cosmological argument for the existence of God.
- Explain the teleological argument for God’s existence.
- What is the ontological argument by Anselm?
- Discuss Aquinas’ Five Ways to prove the existence of God.
- Explain William Paley’s watchmaker analogy.
- Discuss Hume’s critique of design argument.
- Explain Kant’s criticism of ontological proof.
- What is the moral argument for the existence of God?
- Discuss Pascal’s wager.
- Explain Kierkegaard’s view of faith.
- What is the relation between faith and reason in philosophy of religion?
- Discuss the problem of evil and suffering.
- What is the Free Will defense against the problem of evil?
- Explain the concept of immortality of the soul.
- Discuss reincarnation in Indian religions.
- What is the concept of liberation (Moksha) in Hindu philosophy?
- Explain Nirvana in Buddhism.
- What is the Islamic concept of Tawhid?
- Discuss the Christian concept of Trinity.
- Explain Feuerbach’s projection theory of religion.
- Discuss Marx’s view of religion as “opium of the people.”
- Explain Freud’s psychoanalytic view of religion.
- What is Durkheim’s functional theory of religion?
- Discuss Weber’s view on religion and capitalism.
- Explain the role of religion in contemporary society.
Conclusion
Philosophy Optional for UPSC demands analytical clarity and a strong grasp over both Indian and Western traditions. The above 100 questions, structured as per the UPSC syllabus, provide comprehensive practice covering epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, socio-political thought, and philosophy of religion. Regular practice of such questions will help aspirants write balanced and well-structured answers in the examination.
Also Visit – Best IAS Coaching in India
For Answer Writing Techniques – Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE

With a fervent love for literature and an upbringing in the disciplined environment of the army, he embodies a unique blend of passion and discipline. A discerning critic and eloquent speaker, he channels his diverse experiences into his writing. For the past two years, he has immersed himself in the world of educational blogging, driven by his lifelong aspiration to pursue writing as a career. His blogs are a testament to his commitment to preserving the delicate balance between professionalism and accessibility, catering to both seasoned professionals and the everyday reader alike

