Introduction
Chemistry as an optional subject for UPSC Civil Services offers a wide range of theoretical and application-based concepts. It requires clarity in fundamentals, problem-solving ability, and structured preparation. To help aspirants, we have compiled 100 important questions divided according to chapters of the UPSC Chemistry syllabus. These questions will help candidates practice effectively and focus on key areas.
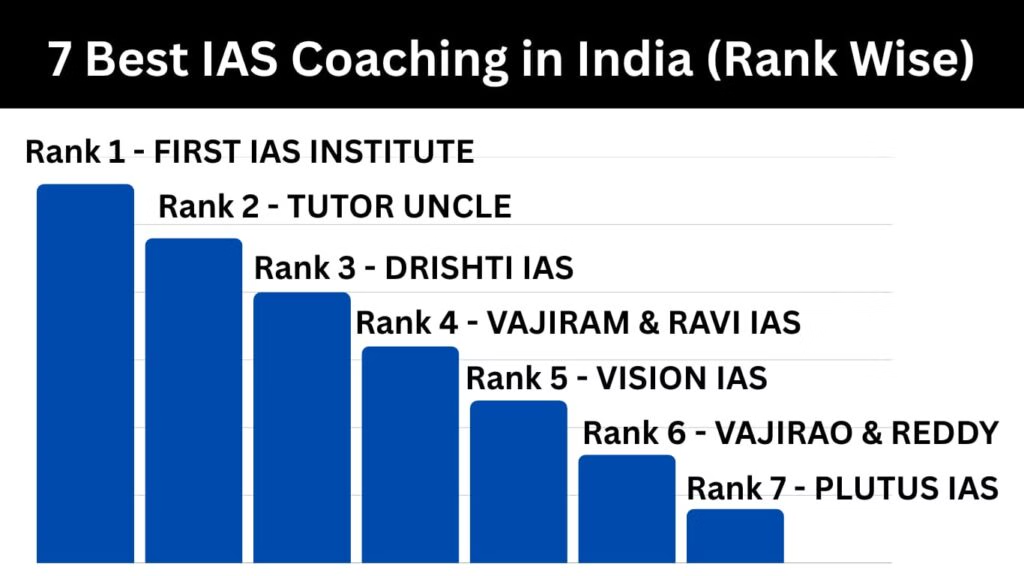
For UPSC Coaching , Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE (India’s Top IAS Coaching)
Chapter 1: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
- Explain the concept of quantum numbers and their significance.
- Discuss the applications of Schrödinger’s wave equation in atomic structure.
- Derive the energy expression for a hydrogen-like atom.
- Explain the shapes of s, p, and d orbitals with diagrams.
- What is Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity? Illustrate with examples.
- Discuss the concept of hybridization with examples of sp, sp2, and sp3.
- Explain the molecular orbital theory of bonding in diatomic molecules.
- Compare valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory.
- What is hydrogen bonding? Discuss its significance.
- Explain VSEPR theory and predict the shapes of common molecules.
Chapter 2: States of Matter and Solid State
- Derive the ideal gas equation and discuss its limitations.
- Explain the van der Waals equation of state.
- What is the concept of compressibility factor?
- Discuss the kinetic theory of gases.
- Explain the types of crystalline solids with examples.
- What is Bragg’s law of X-ray diffraction?
- Explain different types of crystal defects.
- Derive the expression for mean free path of a gas molecule.
- Discuss the liquid crystals and their applications.
- Explain F-centres and their significance in solid-state chemistry.
3: Thermodynamics and Chemical Equilibrium
- State and explain the first law of thermodynamics.
- What is enthalpy of formation?
- Derive the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation.
- Explain entropy and its significance in spontaneity.
- Derive the Clausius-Clapeyron equation.
- Explain the concept of fugacity.
- What is chemical potential?
- Explain the concept of equilibrium constant and its relation with Gibbs free energy.
- Discuss Le Chatelier’s principle with examples.
- Derive the Van’t Hoff isotherm.
Chapter 4: Electrochemistry and Chemical Kinetics
- Explain the Nernst equation and its applications.
- What is electrode potential?
- Derive the expression for cell potential.
- Discuss the applications of electrochemical series.
- Explain different types of electrochemical cells.
- What is the Arrhenius theory of reaction rates?
- Derive the rate law for a first-order reaction.
- Discuss the concept of half-life period.
- Explain the effect of temperature on reaction rate using the Arrhenius equation.
- Discuss the role of catalysts in chemical kinetics.
Chapter 5: Coordination Chemistry and Organometallics
- Explain Werner’s theory of coordination compounds.
- What is the EAN rule? Give examples.
- Discuss the crystal field theory for octahedral complexes.
- Explain the difference between high-spin and low-spin complexes.
- What is ligand field theory?
- Discuss the applications of coordination compounds in industry.
- What are organometallic compounds?
- Explain the role of Grignard reagents in organic synthesis.
- Discuss the bonding in metal carbonyls.
- What is hapticity in organometallic chemistry?
6: Inorganic Chemistry
- Discuss the periodic trends in ionization energy.
- Explain the structure and bonding in diborane.
- What is allotropy? Give examples from Group 16 elements.
- Discuss the preparation and properties of interhalogen compounds.
- Explain the chemistry of transition elements.
- What is lanthanide contraction?
- Discuss the actinides and their oxidation states.
- What are silicones? Discuss their applications.
- Explain the concept of acids and bases according to Lewis theory.
- Discuss the applications of zeolites.
Chapter 7: Organic Chemistry – Basic Principles
- Explain inductive, mesomeric, and hyperconjugation effects.
- What is resonance? Give examples.
- Discuss the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
- Differentiate between SN1 and SN2 mechanisms.
- Explain the concept of aromaticity with examples.
- Discuss electrophilic substitution in benzene.
- Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation.
- What are carbenes and free radicals?
- Discuss the stereochemistry of alkenes.
- Explain optical isomerism with examples.
Chapter 8: Organic Chemistry – Functional Groups
- Discuss the reactions of alcohols.
- What is Kolbe’s reaction?
- Explain the mechanism of Cannizzaro reaction.
- Discuss the chemistry of aldehydes and ketones.
- What is the mechanism of haloform reaction?
- Discuss the reactions of carboxylic acids.
- Explain Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction.
- What are amino acids? Discuss their properties.
- Explain the concept of peptide bond.
- What are carbohydrates? Explain their classification.

9: Physical Chemistry – Surface and Colloids
- Explain adsorption isotherms.
- Discuss the Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
- What is the Langmuir adsorption model?
- Explain the concept of catalysis.
- Discuss enzyme catalysis.
- What are colloids? Discuss their properties.
- Explain electrophoresis and its applications.
- Discuss emulsions and their uses.
- What is the Tyndall effect?
- Explain the role of colloids in medicine.
Chapter 10: Analytical and Applied Chemistry
- Explain the principle of chromatography.
- What are different types of chromatography techniques?
- Discuss the principle of spectroscopy.
- Explain UV-Visible spectroscopy and its applications.
- Discuss the working of IR spectroscopy.
- What is nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy?
- Explain the principle of mass spectrometry.
- What are the applications of X-ray spectroscopy?
- Discuss the principles of gravimetric analysis.
- Explain the role of chemistry in environmental protection.
Conclusion
Chemistry Optional in UPSC demands both conceptual clarity and practice with application-based questions. The above 100 questions cover all key chapters of the UPSC Chemistry syllabus, from atomic structure to applied chemistry. Consistent practice of such questions will help aspirants sharpen their analytical skills, improve writing quality, and enhance their ability to integrate theory with applications.
For Answer Writing Techniques – Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE

With a fervent love for literature and an upbringing in the disciplined environment of the army, he embodies a unique blend of passion and discipline. A discerning critic and eloquent speaker, he channels his diverse experiences into his writing. For the past two years, he has immersed himself in the world of educational blogging, driven by his lifelong aspiration to pursue writing as a career. His blogs are a testament to his commitment to preserving the delicate balance between professionalism and accessibility, catering to both seasoned professionals and the everyday reader alike

