Government schemes are a vital part of UPSC preparation because they link policy, governance, and social development. Questions based on schemes appear in Prelims, Mains, and even in Essay topics.
From 2014 to 2025, India has witnessed an unprecedented number of welfare and reform schemes across sectors—health, education, infrastructure, agriculture, employment, and digital governance. This blog presents a chronological overview of major schemes, highlighting their launch year, objectives, and evolution of all Important Government Schemes for UPSC Exam.
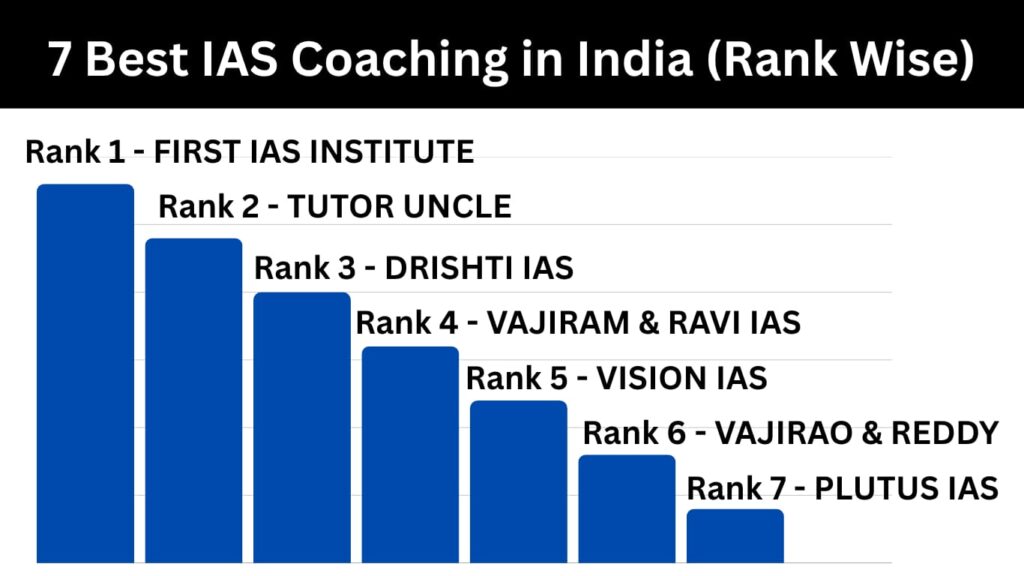
Read More : 7 Best IAS Coaching in India for Hindi Medium
1. Introduction – Why Study Government Schemes for UPSC?
- Schemes show the policy priorities of the government.
- They link budget allocations with real-world outcomes.
- In Mains, schemes are often used as case studies to support answers.
- Many are launched or revamped to address pressing social/economic issues.
2. Chronological Overview of Key Schemes (2014–2025)
2014
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- Objective: Universal access to banking.
- Achievements: Over 50 crore bank accounts opened by 2025.
- UPSC relevance: Financial inclusion, DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer).
- Soil Health Card Scheme
- Objective: Provide soil nutrient status to farmers.
- Importance: Agriculture productivity boost.
2015
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY)
- Low-cost accident insurance for citizens.
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY)
- Low-cost life insurance for citizens.
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
- Focus on unorganised sector pensions.
- Digital India Programme
- Aim: Digital infrastructure, governance, and services.
2016
- Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- LPG connections to women from BPL households.
- Achievements: Over 9 crore beneficiaries by 2025.
- UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik)
- Regional air connectivity scheme.
- Stand-Up India Scheme
- Support for SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
2017
- Saubhagya Scheme
- Electrification of all willing households.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) – Revised version
- Crop insurance against natural calamities.
2018
- Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY
- World’s largest government-funded health insurance programme.
- Gobardhan Yojana
- Waste-to-wealth initiative using bio-gas.
2019
- Jal Jeevan Mission
- Tap water connection to every rural household by 2024.
- Achievement: Extended target to 2026 for remote areas.
- PM-Kisan Samman Nidhi
- ₹6,000 per year income support to farmers.
2020
- PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY)
- Free foodgrain distribution during COVID-19.
- Extended in phases till 2023.
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)
- Digital health ID for all citizens.
Read More : 10 Best IAS Coaching in India
2021
- PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Integrated infrastructure development.
- E-Shram Portal
- Database for unorganised sector workers.
2022
- PM-DevINE (Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East)
- Infrastructure and livelihood projects in the North East.
- National Green Hydrogen Mission (Phase 1)
- Promoting renewable hydrogen production.

2023
- PM Vishwakarma Scheme
- Support for traditional artisans and craftspeople.
- PM SHRI Schools
- Model schools showcasing NEP 2020 implementation.
2024
- PM Awas Yojana (Urban & Rural) – Phase 3
- Focus on affordable housing for urban slum dwellers.
- Digital Krishi Mission
- Data-driven agriculture planning.
2025
- Digital Krishi Mission 2.0
- Expansion with AI-based crop monitoring.
- Green Hydrogen Mission – Phase 2
- Scaling up production and export capacity.
- PM Ujjwala 2.0 Expansion
- Additional benefits: 3 free LPG refills annually.
3. Historical Trends in Scheme Launches
- 2014–2016: Focus on financial inclusion, basic amenities (banking, LPG, insurance).
- 2017–2019: Shift to health, rural infrastructure, and water.
- 2020–2021: COVID-related welfare and digital initiatives.
- 2022–2025: Push toward green growth, digital economy, and targeted social welfare.
4. Budget Allocation Growth (2014 vs 2025)
| Year | Social Sector Spending (₹ crore) | No. of Schemes |
|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2,45,000 | ~50 |
| 2020 | 4,20,000 | ~70 |
| 2025 | 6,80,000 | ~90 |
5. Common Features of Schemes
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mechanism.
- Digital integration – Aadhaar linkage.
- Convergence of schemes – e.g., PMJDY accounts linked to insurance and pensions.
- Focus on inclusive and targeted delivery.
6. UPSC Relevance
Prelims
- Launch year and ministry.
- Beneficiary groups.
- Objectives and coverage.

Mains
- Critical analysis of implementation.
- Role in achieving SDGs.
- Impact on poverty alleviation and human development.
7. Possible UPSC Questions
Prelims MCQ Example
Which of the following schemes aim at providing pension to unorganised sector workers?
- Atal Pension Yojana
- PMJDY
- PMVVY
Answer: 1 and 3 only.
Mains Question Example
“Discuss the role of government schemes launched since 2014 in achieving financial inclusion in India.”
8. Conclusion
The decade from 2014 to 2025 marks a transformative period in India’s welfare policy—moving from basic service delivery to digitally-driven, sustainable, and targeted interventions. For UPSC aspirants, remembering every detail is less important than understanding patterns, priorities, and the socio-economic context in which these schemes operate.
Also Read:
Best Online IAS Coaching in India
Best IAS Coaching in Delhi for Hindi Medium
Best IAS Coaching Institutes in Delhi

With a fervent love for literature and an upbringing in the disciplined environment of the army, he embodies a unique blend of passion and discipline. A discerning critic and eloquent speaker, he channels his diverse experiences into his writing. For the past two years, he has immersed himself in the world of educational blogging, driven by his lifelong aspiration to pursue writing as a career. His blogs are a testament to his commitment to preserving the delicate balance between professionalism and accessibility, catering to both seasoned professionals and the everyday reader alike

