Description
Political Science and International Relations (PSIR) is one of the most popular optional subjects for the UPSC Civil Services Examination. It is chosen by aspirants due to its overlap with General Studies papers, Essay, and current affairs. The subject is divided into four papers – Political Theory and Thought, Indian Government and Politics, Comparative Politics and International Relations, and India’s Foreign Policy. Below is a compilation of 100 important practice questions, divided chapter-wise as per the UPSC syllabus. These questions will help aspirants revise concepts thoroughly and prepare strategically for the examination.
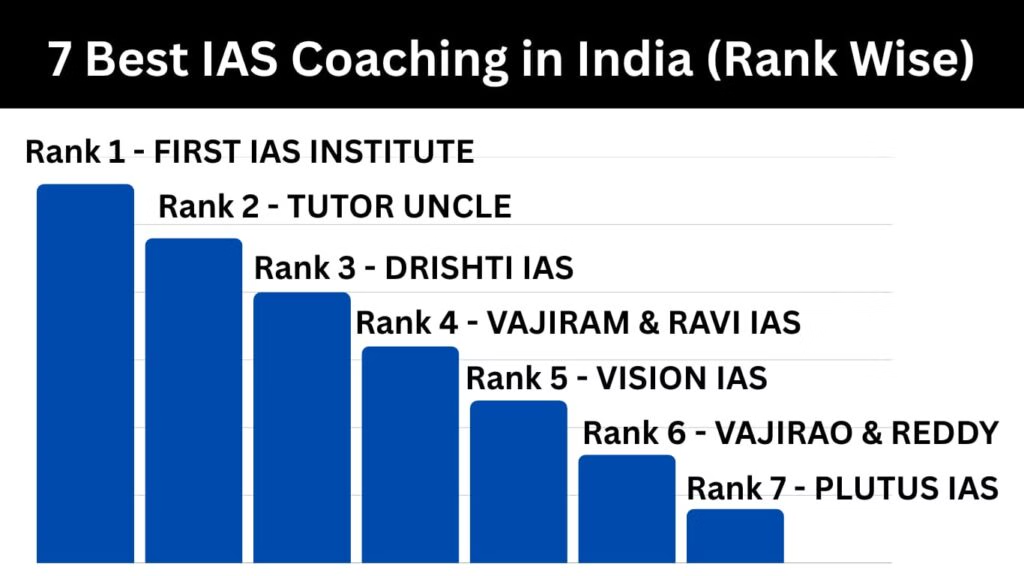
For UPSC Coaching , Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE (India’s Top IAS Coaching)
Chapter 1: Political Theory and Thought
- Define political theory and discuss its relevance in contemporary society.
- Distinguish between normative and empirical political theory.
- Discuss the contribution of Plato to political thought.
- Explain Aristotle’s theory of justice.
- Examine Machiavelli’s views on statecraft and politics.
- Discuss Hobbes’ concept of social contract.
- Compare Locke’s and Rousseau’s social contract theories.
- Evaluate Marx’s critique of capitalism.
- Explain John Stuart Mill’s concept of liberty.
- Discuss the feminist critique of political theory.
- Explain the concept of power according to Steven Lukes.
- What is sovereignty? Discuss its types and relevance today.
- Differentiate between liberalism, socialism, and conservatism.
- Discuss Rawls’ theory of justice.
- Explain communitarian critiques of liberalism.
- Evaluate Bentham’s utilitarianism.
- Discuss Gramsci’s theory of hegemony.
- Examine Hannah Arendt’s concept of totalitarianism.
- Explain the postmodernist critique of political theory.
- Write short notes on the contributions of Indian political thinkers like Kautilya and Gandhi.
Chapter 2: Indian Government and Politics
- Discuss the philosophical basis of the Indian Constitution.
- Explain the significance of the Preamble.
- Critically examine the Fundamental Rights.
- Discuss the Directive Principles of State Policy and their relevance.
- Explain the concept of basic structure of the Constitution.
- Discuss the role of Parliament in India’s democracy.
- Examine the powers and functions of the President of India.
- Discuss the role of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers.
- Critically analyze the position of the Governor.
- Explain the composition and jurisdiction of the Supreme Court.
- Discuss judicial activism and judicial restraint.
- Evaluate the working of federalism in India.
- Discuss the significance of the Finance Commission.
- Examine the role of the Election Commission.
- Discuss the challenges to coalition politics in India.
- Examine the role of caste in Indian politics.
- Discuss the role of regional parties in Indian politics.
- Explain the role of pressure groups and interest groups.
- Discuss the nature of Indian secularism.
- Examine recent constitutional amendments and their significance.
3: Comparative Politics
- Explain the scope and significance of comparative politics.
- Discuss the traditional and modern approaches to comparative politics.
- Explain the structural-functional approach by Almond and Powell.
- Discuss Easton’s systems theory.
- Explain dependency theory.
- Discuss the concept of political culture.
- Explain the concept of political socialization.
- Examine the theories of modernization.
- Compare parliamentary and presidential systems.
- Discuss the features of federal and unitary systems.
- Examine the nature of party systems in different countries.
- Explain the concept of interest articulation and aggregation.
- Discuss the role of bureaucracy in developing countries.
- Compare liberal democracies with authoritarian regimes.
- Discuss the concept of globalization and its impact on politics.
- Examine the role of military in politics.
- Discuss the process of democratization in the developing world.
- Explain the challenges of multiculturalism.
- Examine the relationship between civil society and the state.
- Discuss the concept of governance and good governance.
Chapter 4: International Relations
- Explain the idealist and realist approaches to international relations.
- Discuss the concept of national interest.
- Examine the balance of power theory.
- Explain the concept of collective security.
- Discuss the role of the United Nations in maintaining international peace.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of peacekeeping operations.
- Discuss the concept of nuclear deterrence.
- Examine the Non-Aligned Movement and its relevance today.
- Discuss the impact of globalization on international relations.
- Explain the concept of global governance.
- Examine the role of WTO in world trade.
- Discuss the significance of BRICS.
- Evaluate the role of IMF and World Bank.
- Discuss the concept of South-South cooperation.
- Explain the causes and consequences of terrorism.
- Examine the challenges of climate change in international politics.
- Discuss cyber security as a global issue.
- Explain the role of NGOs in global governance.
- Discuss the concept of human rights in international relations.
- Examine the challenges of migration and refugees.

Chapter 5: India’s Foreign Policy
- Discuss the basic principles of India’s foreign policy.
- Examine the role of Nehru in shaping India’s foreign policy.
- Discuss India’s policy of non-alignment.
- Evaluate the relevance of Panchsheel principles.
- Examine India-China relations.
- Discuss India’s role in SAARC.
- Examine India’s relations with the United States.
- Discuss India’s relations with Russia.
- Examine India’s role in BRICS.
- Discuss India’s Act East policy.
- Evaluate India’s engagement with the European Union.
- Examine India’s relations with West Asia.
- Discuss India’s relations with African countries.
- Examine the role of diaspora in India’s foreign policy.
- Discuss India’s role in the United Nations.
- Evaluate India’s nuclear policy.
- Examine India’s relations with neighboring countries.
- Discuss India’s role in global climate negotiations.
- Evaluate the challenges facing India’s foreign policy.
- Discuss the future prospects of India’s foreign policy in a multipolar world.
Conclusion
The above compilation of 100 questions covers the entire UPSC Political Science and International Relations (PSIR) syllabus systematically. Aspirants are encouraged to use these questions for regular answer writing practice, integrating both static concepts and current affairs examples. This approach not only sharpens conceptual clarity but also improves answer writing skills – both essential for scoring high in UPSC Civil Services Examination.
Also Visit – Best IAS Coaching in India
For Answer Writing Techniques – Join FIRST IAS INSTITUTE

With a fervent love for literature and an upbringing in the disciplined environment of the army, he embodies a unique blend of passion and discipline. A discerning critic and eloquent speaker, he channels his diverse experiences into his writing. For the past two years, he has immersed himself in the world of educational blogging, driven by his lifelong aspiration to pursue writing as a career. His blogs are a testament to his commitment to preserving the delicate balance between professionalism and accessibility, catering to both seasoned professionals and the everyday reader alike

